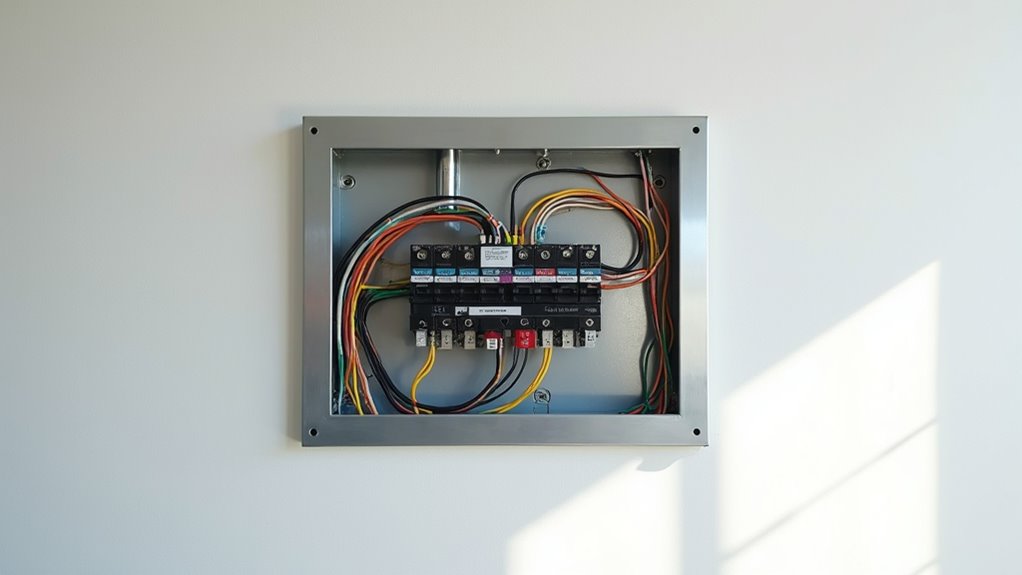
Understanding your home’s electrical panel is essential for managing electricity safely. This metal enclosure houses circuit breakers that distribute power from the utility to your home. The main breaker regulates overall supply, while individual breakers protect specific circuits. If you notice frequent tripping or flickering lights, it might be time to upgrade your panel. Regular maintenance can further guarantee safety and efficiency. Keep going to discover more about the components and care of your electrical panel.
Key Takeaways
- An electrical panel houses circuit breakers to distribute electricity from the utility company to your home safely.
- The main circuit breaker regulates overall power supply, while individual circuit breakers protect specific circuits.
- Regular maintenance and inspection of the panel can prevent overloads and ensure safety.
- Signs like frequent tripping or overheating indicate that your panel may need an upgrade or repair.
- Keeping a clearance of 36 inches around the panel enhances safety and minimizes hazards.
What Is an Electrical Panel?

An electrical panel, often called a breaker box, is the heart of your home’s electrical system. This metal enclosure houses circuit breakers that control the distribution of electricity throughout your home. The panel typically contains a main circuit breaker, which regulates the overall power supply, and individual circuit breakers that manage electricity flow to specific areas or appliances. Modern electrical panels usually provide between 100 to 200 amps, with each circuit designed to carry between 15 to 20 amps. Energy-efficient technology is also important in modern electrical systems, as it can improve the overall performance of devices connected to the electrical panel. Additionally, maintaining an organized space around your panel can enhance focus and productivity, ensuring safe access and minimizing hazards. The choice of HEPA filters in air purifiers can also impact indoor air quality and overall comfort in your home.
Your panel connects to utility service wires, ensuring safe electricity distribution. In the event of overloads or short circuits, breakers trip automatically to prevent hazards, enhancing electrical safety. Color accuracy is also crucial in home systems, as it can impact the performance of devices connected to the electrical panel. You’ll often find these panels in basements, garages, or utility rooms.
How Does an Electrical Panel Work?
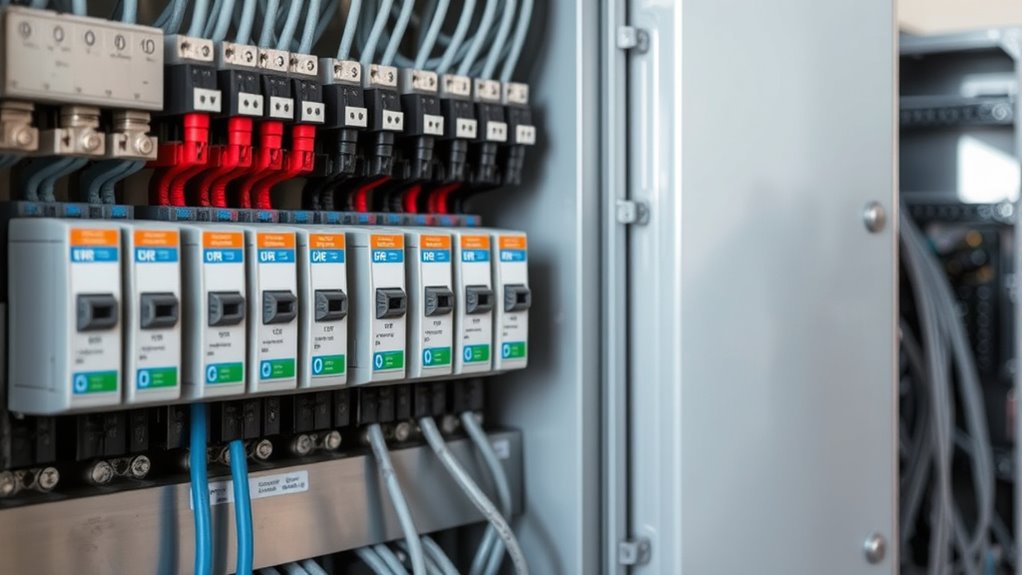

Understanding how your electrical panel works is crucial for maintaining a safe and efficient home. The electrical panel, or breaker box, distributes power from the utility company to various circuits. It starts with the main breaker, controlling the overall power supply. Inside, circuit breakers act as safety devices, tripping during overloads or short circuits to prevent damage. Each breaker manages a specific electrical load, with options typically ranging from 15 to 200 amps. Grounding wires guarantee safety, directing stray currents away. Additionally, ensuring that your electrical panel is in good condition is important to prevent mechanical failures that can lead to electrical hazards. Regular maintenance can help reduce the risk of pollutants from wood-burning affecting your home’s air quality. Understanding the importance of safety devices in your electrical panel can further enhance your home’s safety. An effective electrical panel also ensures time-efficient application of power, reducing the risk of overloads.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Main Breaker | Controls power supply |
| Circuit Breakers | Protect circuits from overloads |
| Grounding Wires | Direct stray currents |
| Electrical Load | Power usage by devices |
| Safety Devices | Prevent fire hazards |
Components of an Electrical Panel
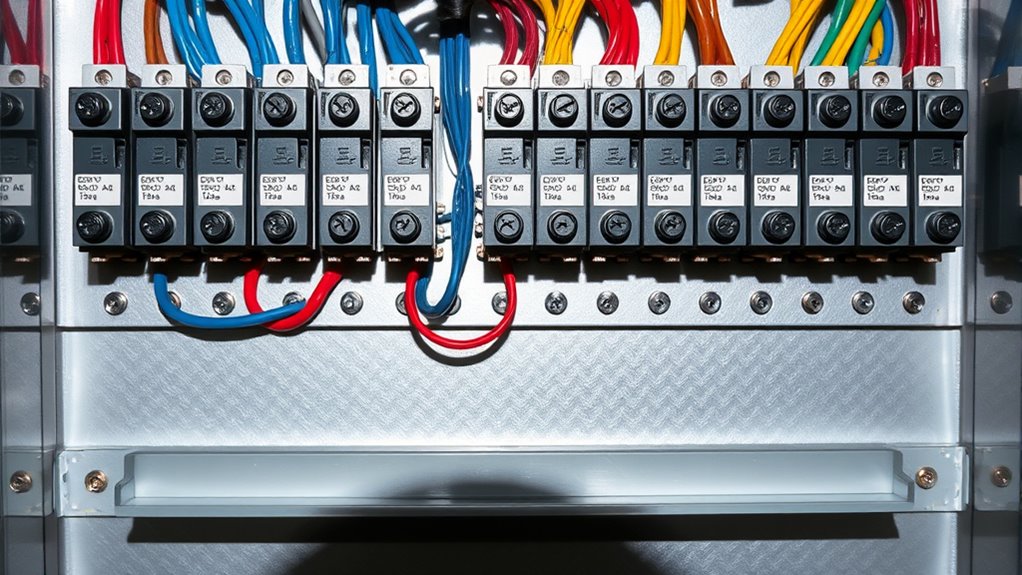
Here are the main components:
- Main Circuit Breaker: Controls the overall power supply and indicates total amperage ratings, typically between 100 and 200 amps. Modern homes often require a high-capacity electrical panel to accommodate increased energy demands, especially as the use of solar panels becomes more prevalent.
- Circuit Breakers: Protect specific circuits, ranging from 15 to 50 amps, with single-pole providing 120 volts and double-pole supplying 240 volts. It is essential to regularly check these breakers to ensure they are functioning properly and providing adequate protection.
- Bus Bars: Distribute power from the main breaker to individual circuit breakers, while neutral and ground wires connect to neutral and ground bars, ensuring safe electricity return paths. Additionally, GFCI and AFCI breakers add vital protection against electrical shocks and fire hazards. Understanding the importance of a home security system can complement your electrical safety by safeguarding against potential intrusions that could jeopardize your electrical infrastructure.
Signs You Should Upgrade or Repair Your Electrical Panel

Recognizing when it’s time to upgrade or repair your electrical panel can prevent safety hazards and guarantee your home meets modern electrical demands.
If you notice frequent tripping of circuit breakers, it’s a clear sign your electrical panel might be overloaded. Panels over 20 years old or using fuses need an upgrade to meet safety standards. In addition, diversifying investments can help ensure you have the funds necessary for such upgrades. To improve efficiency and safety, consider implementing efficient payment solutions that streamline your financial management.
Flickering lights when using multiple appliances indicate inadequate power distribution, while warm to the touch or discolored panel boxes suggest overheating circuits that pose fire risks. Furthermore, maintaining a budget plan can help you allocate funds for necessary repairs more effectively.
Additionally, watch for signs of corrosion near the electrical panel and any burning smells—these require immediate attention from a qualified electrician.
Prioritizing these signs guarantees your home remains safe and functional. Furthermore, understanding the division of retirement accounts can also be crucial when planning for future financial stability after major home repairs.
How to Safely Maintain Your Electrical Panel
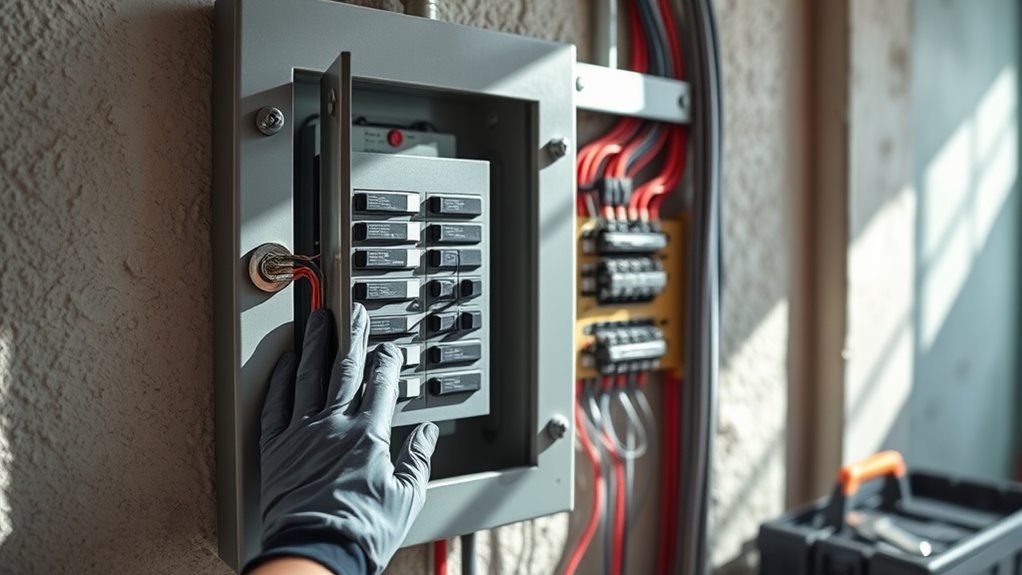

Maintaining your electrical panel is essential for guaranteeing safety and efficiency in your home. Regular maintenance can help you identify potential issues before they escalate.
Here are three key steps to follow:
- Inspect your electrical panel every three to five years with a licensed electrician. This guarantees all components function correctly and safely, similar to how consistent maintenance of an air purifier improves performance. Regular inspections can also prevent major repairs that may arise from neglected components, especially as energy efficiency ratings can indicate how well your electrical system performs.
- Maintain a clearance of at least 36 inches around the electrical panel. This not only complies with safety regulations but also allows for quick access during emergencies, just as proper placement of air purifiers enhances air circulation.
- Test circuit breakers annually. If you notice non-resetting or frequently tripping breakers, it may indicate underlying electrical wiring issues that need immediate attention. Additionally, ensuring your home’s electrical system is up to code is vital for preventing electric vehicle fires that can occur from faulty wiring. Regular checks are crucial for maintaining optimal usage to ensure safety and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to Read a Home Electrical Panel?
To read a home electrical panel, start by locating the main circuit breaker at the top; it controls your power supply and shows total amperage capacity.
Next, check the labeled circuit breakers to identify which areas or appliances they serve. For single-pole breakers, expect 120 volts, while double-pole ones supply 240 volts for larger appliances.
Regularly inspect for any signs of damage, ensuring breakers are in the “ON” position for safe operation.
How Do I Know if I Have 100 or 200 Amp Service to My House?
To find out if you’ve got 100 or 200 amp service, check your main circuit breaker.
It’s usually labeled at the top of your electrical panel. If you see a larger double-pole breaker, it’s likely 200 amps.
Also, count the number of circuits; more than 20 usually indicates 200 amps.
If you’re still unsure, it’s best to call a licensed electrician for a thorough inspection and to guarantee everything’s up to code.
What Is the 80% Rule on an Electrical Panel?
The 80% rule suggests you shouldn’t load your electrical circuits beyond 80% of their rated capacity.
For example, if you have a 20-amp circuit, aim for a maximum continuous load of 16 amps. This helps prevent overheating and reduces the risk of tripping breakers or electrical fires.
What Do the Numbers on My Electrical Panel Mean?
Did you know that most residential electrical panels typically support between 20 to 40 circuits?
The numbers on your electrical panel indicate the amperage ratings of your main circuit breaker and individual breakers. For example, you might see ratings from 15 to 50 amps for each circuit, showing the maximum current allowed.
The main breaker usually ranges from 60 to 400 amps, reflecting your home’s overall capacity for electrical usage.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding your home’s electrical panel is like opening a treasure chest of safety and efficiency. By knowing its components and how it works, you can guarantee your home runs smoothly and safely. If you notice signs that it’s time for an upgrade or repair, don’t hesitate to act—your family’s safety depends on it! Regular maintenance can keep your electrical panel buzzing like a well-oiled machine, giving you peace of mind for years to come.









